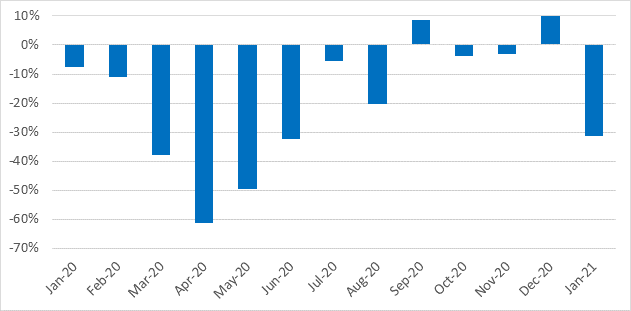
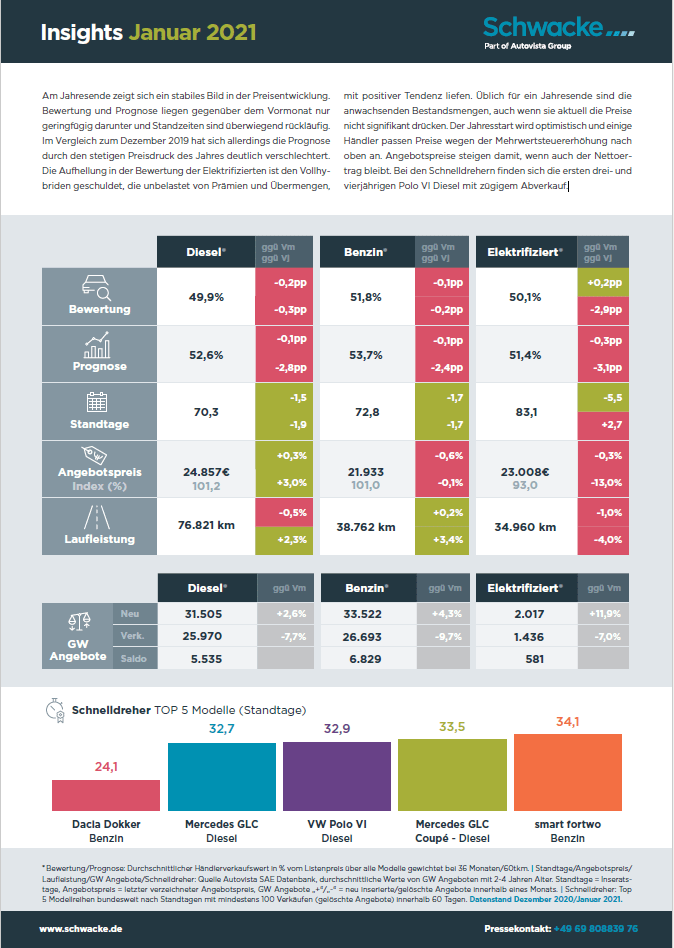
Andreas Geilenbrügge, Head of Valuations and Insights bei Schwacke, untersucht, welche Auswirkungen die bevorstehenden Änderungen bestimmter Fahrzeugsubventionen in Deutschland haben könnten.
Seit 2020 im Zuge der Pandemie die staatliche Innovationsprämie verdoppelt wurde, gehen in Deutschland die subventionierten Antriebsarten BEV und PHEV durch die Decke. Die Zulassungen vollelektrischer Modelle haben sich 2020 im Vergleich zu 2019 mehr als verdreifacht, Plug-Ins sogar fast verfünffacht. Und der Neuwagentrend geht für die Stromer in 2021 immer noch bergauf.
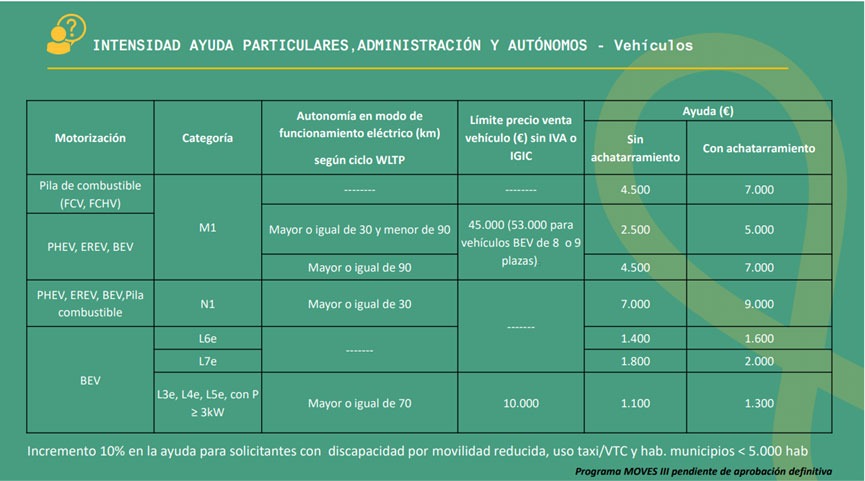
Nun hatte die Bundesregierung sich frühzeitig darauf verständigt, dass dieses Prämienniveau bis Ende 2025 beibehalten und entsprechende Finanzierung bereitgestellt wird. Das zugehörige Förder-Regularium allerdings ist Deutschland-typisch komplex. Neben der unterschiedlichen Förderung von günstigen (Nettolistenpreis unter 40.000€) und teureren Modellen (Nettolistenpreis bis 65.000€) hat man noch weitere Bedingungen eingebaut, von denen eine nun ab 2022 einigen wenigen Modellen den Förderanspruch eventuell versagen wird.
Für Plug-In Hybride steigt die reinelektrische Mindestreichweite von bisher 40km auf 60km für Fahrzeuganschaffungen ab dem 1. Januar 2022. Zwar gilt immer noch die Förderfähigkeit, wenn dabei maximal 50g CO2-Ausstoß pro 100km erreicht werden, aber es gibt Fahrzeuge, die aktuell diesen CO2-Ausstoß übertreffen, während sie die derzeit gültigen 40km Reichweite schaffen.
Für die Kombination weniger als 60km Reichweite und mehr als 50g CO2 ist es also ab nächstem Jahr vorbei mit 4.500 bzw. 3.750€ Zuschuss vom Staat. Betroffen sind allerdings eher wenige schwere Fahrzeuge, die sich in beiden Disziplinen – Reichweite und Emission – buchstäblich schwertun und unterhalb der 65.000€ Listenpreisgrenze liegen. Es betrifft einzelne Modellversionen sowohl von Audi, Ford, Jaguar, Jeep, Mercedes, Land Rover, Volvo und VW. Darunter manche Exoten wie den Wrangler oder Explorer, aber eben auch Versionen gängigerer Modelle wie z.B. den Q8, F-Pace, GLC, Velar, XC90 und Touareg. Ob es so weit kommt, liegt auch in den Händen der Hersteller.
Es müssten rechtzeitig neue elektrische Reichweiten homologiert werden, die die 60km übertreffen, was technisch kein größeres Thema sein dürfte. Allerdings wird man sicher den Taschenrechner zücken und die Kosten für die Homologation gegenrechnen mit einerseits der Hinnahme möglicher Stückzahleinbußen durch die betroffenen Versionen oder alternativ für diese Modelle zusätzliche Vertriebsunterstützung bereitzustellen. Was wir aber vermutlich beobachten werden, sind eifrige Zulassungen dieser Modelle zum Ende des Jahres, um den Förderanspruch zu erhalten und die Produktion auf die Straße zu bringen.
Die Restwerte wird ein möglicher Wegfall der Prämie vermutlich nur geringfügig beeinflussen, da in diesen Preislagen der staatliche Zuschuss eher einen kleineren Effekt hat. Schon eher die kurzfristig anwachsenden Mengen auf dem Gebrauchtmarkt, verursacht durch die voraussichtlichen Zulassungsaktionen Ende des Jahres, könnten je nach Größenordnung Volumen- und damit Preisdruck erzeugen. In jedem Fall wird es interessant zu beobachten, was mit diesen Modellen passiert.
Dieser Inhalt wird Ihnen präsentiert von Autovista24.



 Schließen
Schließen